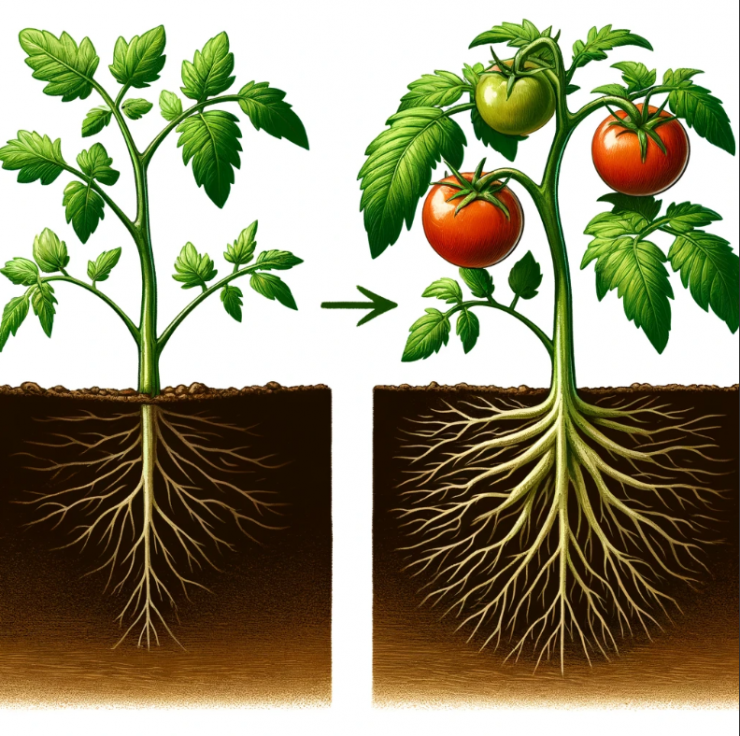
Growing tomatoes can be incredibly rewarding, especially when you harvest a bountiful crop of large, juicy fruits. While there are many tips and techniques for boosting tomato yields, one particularly effective method involves planting your tomato seedlings on their side. This unconventional approach is designed to stimulate extensive root growth, leading to stronger plants and significantly larger yields. Let’s dive into how and why this technique works.
Tomato plants are capable of developing roots along their stems, a trait known as adventitious root growth. When you lay the seedling on its side and bury the stem, you expose more surface area to the soil, which encourages the formation of additional roots. These extra roots can absorb more nutrients and water, providing the plant with better support and nourishment, which is crucial for producing a large crop.
Step-by-Step Guide to Planting Tomatoes Sideways
1.Choose the Right Seedlings
Start with healthy, young tomato seedlings that are 6-8 inches tall. Look for plants with a sturdy stem and vibrant green leaves.
2.Prepare the Soil
Ensure your garden bed or container is filled with rich, well-draining soil. Amend the soil with compost and a balanced fertilizer to provide initial nutrients for your tomatoes.
3.Dig a Trench
Instead of a deep hole, dig a shallow trench about 3-4 inches deep. The length should accommodate the entire stem of the tomato seedling, except for the top few inches of leaves.
4.Lay the Seedling Down
Remove any lower leaves from the stem, leaving only the topmost leaves. Lay the seedling horizontally in the trench, gently bending the tip with the leaves upward so it emerges from the soil.
5.Bury the Stem
Fill the trench with soil, covering the entire stem but leaving the top leaves exposed. This buried stem will soon sprout additional roots.
6.Water Thoroughly
Water the newly planted seedling generously to settle the soil around it and help reduce transplant shock.
Additional Tips for Success
Watering: Tomato plants require consistent moisture, especially as they grow larger and start setting fruit. Use mulch to help retain soil moisture and regulate temperature.
Staking: Since your plant will have a significant amount of foliage and, hopefully, fruit, provide support with stakes or cages early on to prevent damage.
Pruning: Remove any suckers (small shoots that grow in the axils of leaves) to encourage more vigorous growth and larger fruits.
Monitoring for Pests and Diseases: Keep an eye out for common tomato pests and diseases. Early detection and treatment can prevent significant damage.
Planting tomatoes on their side is a simple yet effective technique that can lead to impressive yields. By encouraging robust root development, this method helps your tomato plants become more resilient and productive. Give it a try this planting season and watch your tomato garden thrive like never before. Happy gardening!





Add comment